Yunjie Li , Xiaoxiao Hu , Ding Ding , Yuxiu Zou , Yiting Xu , Xuewei Wang , Yin Zhang, Long Chen, Zhuo Chen & Weihong Tan
Nature Communications 8, Article number: 15653 (2017), doi:10.1038/ncomms15653
Abstract:
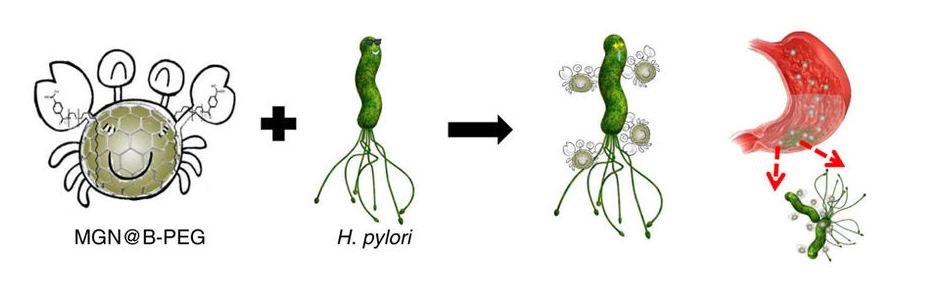
Helicobacter pylori infection is implicated in the aetiology of many diseases. Despite numerous studies, a painless, fast and direct method for the in situ detection of H. pylori remains a challenge, mainly due to the strong acidic/enzymatic environment of the gastric mucosa. Herein, we report the use of stable magnetic graphitic nanocapsules (MGNs), for in situ targeted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detection of H. pylori. Several layers of graphene as the shell effectively protect the magnetic core from corrosion while retaining the superior contrast effect for MRI in the gastric environment. Boronic-polyethylene glycol molecules were synthesized and modified on the MGN surface for targeted MRI detection. In a mouse model of H. pylori-induced infection, H. pylori was specifically detected through both T2-weighted MR imaging and Raman gastric mucosa imaging using functionalized MGNs. These results indicated that enhancement of MRI using MGNs may be a promising diagnostic and bioimaging platform for very harsh conditions.
全文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15653